Abstract: In this paper, the maximum amount of straight stroke control valve is used. Most manufacturers are analyzing the technical details of the soft sealing structure design of single seat control valve.
1. Introduction The control valve (also called the control valve) is the terminal control element of the process control loop, but it is also a weak link in the system process control loop. The regulating valve can be divided into three types of regulating type, regulating cutting type and cutting type according to the adjustment type. Among them, the regulating valve of adjusting cut-off type and cut-off type must meet the requirements of ASMEB16.104 VI (namely bubble level). Adjusting and shutting off the type control valve usually adopts the soft seal structure to be able to achieve the VI grade leak quantity request.
2. Structural Analysis 2.1 Traditional single-seat regulating valve soft seal structure design Since the 1980s, with the implementation and implementation of China's reform and opening up policy, some regulating valve manufacturers have introduced the technology and products of well-known foreign control valve manufacturers. The variety and quality of our control valve products have been significantly improved. Among them, the typical CV3000 series control valve from Yamatake Corporation of Japan, such as the typical structure of the HTS single seat adjustment cutoff type control valve (ie soft seal) in the Cv3000 series (Fig. 1). The soft sealing ring of the regulating valve is embedded into the valve stem through the valve head and the screw, and the valve seat is screwed onto the valve body through the threaded connection.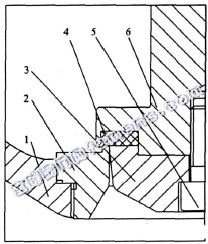 1 Body 2 Valve seat 3 Valve head 4 Soft seal ring 5 screws 6 Valve stem
1 Body 2 Valve seat 3 Valve head 4 Soft seal ring 5 screws 6 Valve stem
When the valve is in the closed state, the convex surface of the valve seat is embedded in the soft seal ring (soft seal ring is usually made of elastic material such as PTFE), where the elastic material deforms to surround the valve seat convex surface, This ensures a reliable sealing effect and at the same time the valve stem does not receive excessive thrust. Thus, it can be seen that the valve can be sealed with only a suitable force when it is closed, and the elastic material itself can also sustain this closing force for a long time. This is particularly relevant for opening long-closed valves. Because the surface of the elastic material is not permanently deformed, it can guarantee the sealing performance when the valve seat and the valve flap are repeatedly opened and closed. In addition, because the valve flap embedded in the elastic material can correct minor deviations in the concentricity of the seal pair, the positional accuracy requirements for the manufacture of the valve flap and the valve seat can be lower.
However, this type of soft seal structure also has some disadvantages. The first is that it is difficult to limit the closing force. Even when the soft-seal ring contacts the valve seat, the closing action cannot be stopped in time. As a result, the elastic material is prone to permanent deformation, especially when the valve is closed for a long time. Soft seal rings are subjected to permanent deformation due to overload pressure for a long period of time, and are easily failed when opened and closed. Secondly, in the valve opening process, due to the throttling effect of the valve flap, the high-speed flow of the medium occurs within a short time after the valve is opened. At this time, the soft seal ring is subjected to a large pressure drop, which will be a soft seal. The surface of the ring is eroded, causing rapid destruction of its surface. Therefore, the soft seal structure is usually limited to use in situations where the pressure drop is less than 3 MPa.
In addition, the structure has great drawbacks in terms of assembly, disassembly and maintenance. Firstly, the soft seal ring is screwed into the valve stem through the valve head and the screw. In order to ensure that the screw does not loosen, it is usually necessary to apply a suitable curing glue on the screw or fix it by riveting or spot welding. The screw, which gives great inconvenience to dismantling and replacing the soft seal ring again. Followed by the threaded connection of the valve seat, the need for special tools to be able to assembly and disassembly, on-site maintenance is extremely inconvenient.
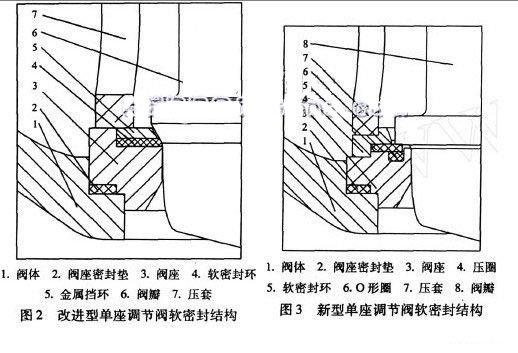
2.2 Improved soft seal structure design With the development of industrial technology, users want to obtain higher quality valves, but also require the use of valves to improve the level of maintenance. This puts forward new requirements for engineers and technicians. In addition to careful design of high-quality and high-level valves, reasonable selection and correct operation, maintenance and demolition of maintenance personnel must be facilitated. And maintenance time is minimized. Thus, for a single seat regulator valve, the improved soft seal design shown in Figure 2 appears. In this structural design, the metal snap ring and the soft seal ring are used to replace the design of the embedded soft seal ring with screws in the conventional structure, and the pressure sleeve and the valve seat seal direct pressure type structure design replace the traditional structural middle valve. Seat with threaded connection design. This design advantage is that when the valve flap and the valve seat reach the final closed position, part of the force applied by the valve flap to the valve seat is borne by the metal retaining ring and is directly transmitted to the valve seat, thus eliminating the damage of the soft sealing ring due to overload. And the metal retaining ring also provides a certain auxiliary sealing effect. The direct-pressure structural design also changed the design of threaded seats that require special tooling to be removed, and assembly and disassembly, on-site repair and replacement are all very convenient.
The improved soft seal structure design also has certain shortcomings. First, once the soft seal ring fails, the metal retaining ring can only play a temporary seal and must be replaced as soon as possible. In addition, if the medium contains solid particles, it is extremely easy to get caught in the middle of the disc and the valve seat, which prevents the valve seat from being sealed and can cause leakage. The surface of the valve seat is then damaged by erosion due to high-speed flushing of the medium.
2.3 The design of a new soft seal structure In order to make up for the deficiencies of the above structure, a new single seat control valve soft seal structure design shown in Figure 3 has emerged.
In the new structure, the seal pair adopts metal seal and PTFE elastic seal double seal design. The metal-sealed valve seat acts as a support to prevent the soft seal ring from being crushed due to excessive pressure. The soft seal ring is supported by the elastic O-ring and is protected by the metal pressure ring. The additional metal pressure ring eliminates the danger of the soft seal element being overloaded. This means that the bubble level can be achieved after 500,000 switches (level VI). Sealed, leaking.
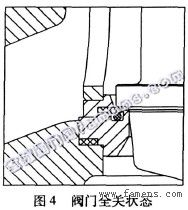
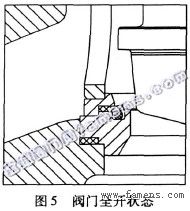
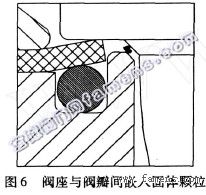
Figure 4 shows the fully closed state of the valve. The metal seal and the elastic seal function simultaneously and the seal is tight and reliable.
Figure 5 shows the fully open state of the valve. The elastic soft seal ring recovers its elasticity.
At the instant when the valve is opened, the turbulence generated by the medium at the outer edge of the seal will cause the vibration of the seal and cause the seal material to fatigue. In the new structure, due to the protection of the flange of the metal seat ring, the soft seal ring will not be flushed by the fluid and will not be easily damaged.
For fluid media with solid particles, the seal structure of the soft seat valve is more important. This is mainly because the solid particles in the medium are easily trapped between the valve plate and the sealing surface of the valve seat, impede the sealing of the valve seat, and may cause leakage. The surface of the valve seat is then subjected to high-speed flushing of the medium. Erosion damage. For the above-mentioned soft valve seat sealing structure with secondary closing effect (Figure 6), even if such particles are trapped between the valve flap and the metal seat of the valve seat, there will be no harm because of the valve flap and The seal between the soft seats still provides a reliable and effective supplementary seal.
3. Conclusion As the harsh conditions of use of valve products continue to increase, the requirements for structural design of valves have also been continuously improved. At the same time, the development of engineering materials has also been promoted. Due to various special demands on the valve, the manufacturer is required to continuously develop new types of sealing components to meet the needs of modern industrial development. The new single-seat control valve soft seal structure design can be successfully applied to the valve diameter of 25mm or more, the pressure drop can reach 30MPa, with fire safety, reliable sealing, assembly, disassembly and easy maintenance, etc., worthy of widespread promotion and application.
1. Introduction The control valve (also called the control valve) is the terminal control element of the process control loop, but it is also a weak link in the system process control loop. The regulating valve can be divided into three types of regulating type, regulating cutting type and cutting type according to the adjustment type. Among them, the regulating valve of adjusting cut-off type and cut-off type must meet the requirements of ASMEB16.104 VI (namely bubble level). Adjusting and shutting off the type control valve usually adopts the soft seal structure to be able to achieve the VI grade leak quantity request.
2. Structural Analysis 2.1 Traditional single-seat regulating valve soft seal structure design Since the 1980s, with the implementation and implementation of China's reform and opening up policy, some regulating valve manufacturers have introduced the technology and products of well-known foreign control valve manufacturers. The variety and quality of our control valve products have been significantly improved. Among them, the typical CV3000 series control valve from Yamatake Corporation of Japan, such as the typical structure of the HTS single seat adjustment cutoff type control valve (ie soft seal) in the Cv3000 series (Fig. 1). The soft sealing ring of the regulating valve is embedded into the valve stem through the valve head and the screw, and the valve seat is screwed onto the valve body through the threaded connection.

Figure 1 traditional single-seat regulating valve soft seal structure
When the valve is in the closed state, the convex surface of the valve seat is embedded in the soft seal ring (soft seal ring is usually made of elastic material such as PTFE), where the elastic material deforms to surround the valve seat convex surface, This ensures a reliable sealing effect and at the same time the valve stem does not receive excessive thrust. Thus, it can be seen that the valve can be sealed with only a suitable force when it is closed, and the elastic material itself can also sustain this closing force for a long time. This is particularly relevant for opening long-closed valves. Because the surface of the elastic material is not permanently deformed, it can guarantee the sealing performance when the valve seat and the valve flap are repeatedly opened and closed. In addition, because the valve flap embedded in the elastic material can correct minor deviations in the concentricity of the seal pair, the positional accuracy requirements for the manufacture of the valve flap and the valve seat can be lower.

However, this type of soft seal structure also has some disadvantages. The first is that it is difficult to limit the closing force. Even when the soft-seal ring contacts the valve seat, the closing action cannot be stopped in time. As a result, the elastic material is prone to permanent deformation, especially when the valve is closed for a long time. Soft seal rings are subjected to permanent deformation due to overload pressure for a long period of time, and are easily failed when opened and closed. Secondly, in the valve opening process, due to the throttling effect of the valve flap, the high-speed flow of the medium occurs within a short time after the valve is opened. At this time, the soft seal ring is subjected to a large pressure drop, which will be a soft seal. The surface of the ring is eroded, causing rapid destruction of its surface. Therefore, the soft seal structure is usually limited to use in situations where the pressure drop is less than 3 MPa.
In addition, the structure has great drawbacks in terms of assembly, disassembly and maintenance. Firstly, the soft seal ring is screwed into the valve stem through the valve head and the screw. In order to ensure that the screw does not loosen, it is usually necessary to apply a suitable curing glue on the screw or fix it by riveting or spot welding. The screw, which gives great inconvenience to dismantling and replacing the soft seal ring again. Followed by the threaded connection of the valve seat, the need for special tools to be able to assembly and disassembly, on-site maintenance is extremely inconvenient.
2.2 Improved soft seal structure design With the development of industrial technology, users want to obtain higher quality valves, but also require the use of valves to improve the level of maintenance. This puts forward new requirements for engineers and technicians. In addition to careful design of high-quality and high-level valves, reasonable selection and correct operation, maintenance and demolition of maintenance personnel must be facilitated. And maintenance time is minimized. Thus, for a single seat regulator valve, the improved soft seal design shown in Figure 2 appears. In this structural design, the metal snap ring and the soft seal ring are used to replace the design of the embedded soft seal ring with screws in the conventional structure, and the pressure sleeve and the valve seat seal direct pressure type structure design replace the traditional structural middle valve. Seat with threaded connection design. This design advantage is that when the valve flap and the valve seat reach the final closed position, part of the force applied by the valve flap to the valve seat is borne by the metal retaining ring and is directly transmitted to the valve seat, thus eliminating the damage of the soft sealing ring due to overload. And the metal retaining ring also provides a certain auxiliary sealing effect. The direct-pressure structural design also changed the design of threaded seats that require special tooling to be removed, and assembly and disassembly, on-site repair and replacement are all very convenient.
The improved soft seal structure design also has certain shortcomings. First, once the soft seal ring fails, the metal retaining ring can only play a temporary seal and must be replaced as soon as possible. In addition, if the medium contains solid particles, it is extremely easy to get caught in the middle of the disc and the valve seat, which prevents the valve seat from being sealed and can cause leakage. The surface of the valve seat is then damaged by erosion due to high-speed flushing of the medium.
2.3 The design of a new soft seal structure In order to make up for the deficiencies of the above structure, a new single seat control valve soft seal structure design shown in Figure 3 has emerged.
In the new structure, the seal pair adopts metal seal and PTFE elastic seal double seal design. The metal-sealed valve seat acts as a support to prevent the soft seal ring from being crushed due to excessive pressure. The soft seal ring is supported by the elastic O-ring and is protected by the metal pressure ring. The additional metal pressure ring eliminates the danger of the soft seal element being overloaded. This means that the bubble level can be achieved after 500,000 switches (level VI). Sealed, leaking.



Figure 4 shows the fully closed state of the valve. The metal seal and the elastic seal function simultaneously and the seal is tight and reliable.
Figure 5 shows the fully open state of the valve. The elastic soft seal ring recovers its elasticity.
At the instant when the valve is opened, the turbulence generated by the medium at the outer edge of the seal will cause the vibration of the seal and cause the seal material to fatigue. In the new structure, due to the protection of the flange of the metal seat ring, the soft seal ring will not be flushed by the fluid and will not be easily damaged.
For fluid media with solid particles, the seal structure of the soft seat valve is more important. This is mainly because the solid particles in the medium are easily trapped between the valve plate and the sealing surface of the valve seat, impede the sealing of the valve seat, and may cause leakage. The surface of the valve seat is then subjected to high-speed flushing of the medium. Erosion damage. For the above-mentioned soft valve seat sealing structure with secondary closing effect (Figure 6), even if such particles are trapped between the valve flap and the metal seat of the valve seat, there will be no harm because of the valve flap and The seal between the soft seats still provides a reliable and effective supplementary seal.
3. Conclusion As the harsh conditions of use of valve products continue to increase, the requirements for structural design of valves have also been continuously improved. At the same time, the development of engineering materials has also been promoted. Due to various special demands on the valve, the manufacturer is required to continuously develop new types of sealing components to meet the needs of modern industrial development. The new single-seat control valve soft seal structure design can be successfully applied to the valve diameter of 25mm or more, the pressure drop can reach 30MPa, with fire safety, reliable sealing, assembly, disassembly and easy maintenance, etc., worthy of widespread promotion and application.